A force is a physical entity that is applied to an object in order to displace it. The ultimate effect is a ‘push’ or ‘pull’ that the object experiences. A force is a vector that has both magnitude and direction.
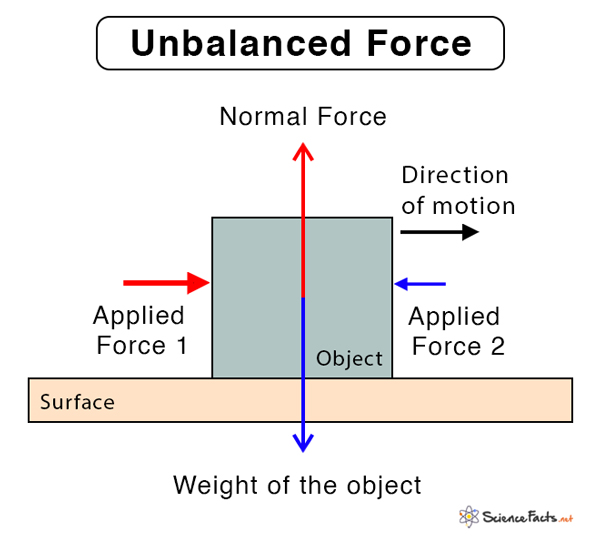
Unbalanced forces refer to a set of forces acting on an object such they affect its motion. When two unequal forces act on an object from opposite sides, there is a net force, called the resultant force. The effect of this force is to either displace or tilt an object. When an unbalanced force is acting on a moving object, it changes the direction or speed.

What happens when an unbalanced force acts on an object?
Here are some facts and characteristics of the unbalanced force. When an unbalanced force acts on an object, the following can happen:
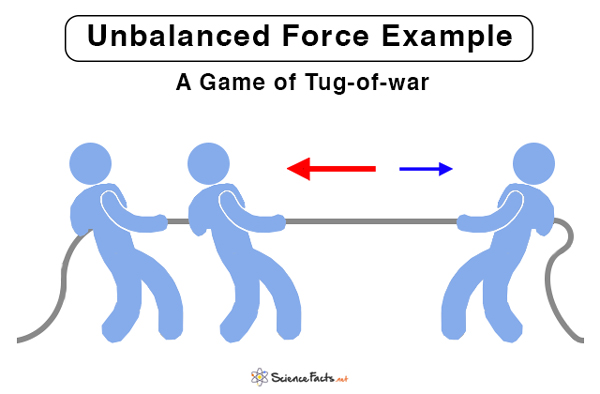
Here are a few examples of the unbalanced force.
Suppose F1 and F2 are two unequal forces acting on an object in opposite directions. Then, by definition of an unbalanced force, the net force acting on the object is non-zero.
For example, a book of mass m is lying on a table. An externally applied force FA acts on it. It overcomes the friction FK and moves with an acceleration a. According to Newton’s second law, the force experienced by the book is given by
As can be seen, the result of unbalanced forces is to accelerate the object.
Ans. It depends upon whether the friction force balances the applied force or not. In static friction, the object remains motionless because the static friction force balances the applied force. In kinetic friction, the object moves against the kinetic friction force in the applied force’s direction. If the object moves with a constant velocity, then the two forces are balanced. If the object moves with acceleration, then the two forces are unbalanced.
ReferencesArticle was last reviewed on Thursday, February 2, 2023
Electron Capture
Neutron Emission
Spectrophotometry
Gamma Decay
We have explained the concept of unbalanced force. In both the images, the red arrow represents a greater force than the blue arrow. Due to a difference in the two forces, the net force on the object is not zero. Therefore, the object experiences an unbalanced force.
RADHIKA says:t depends upon whether the friction force balances the applied force or not. In static friction, the object remains motionless because the static friction force balances the applied force. In kinetic friction, the object moves against the kinetic friction force in the applied force’s direction. If the object moves with a constant velocity, then the two forces are balanced. If the object moves with acceleration, then the two forces are unbalanced.